Pre-build building terminology
Sketch drawings
First set of drawings done by an architect for concept purposes. Often include more elevation sketches with coloured landscaping and other enhancing features.
Construction drawings
Technical, detailed drawings completed by an architect or draught person for construction. A basic set is required for council purposes.
SG diagram
The registered document prepared by the land surveyor showing the property dimensions and corner beakons.
Natural ground level (NGL)
The original ground levels of the site, according to the surveyor document.
Schedule of finishes
Detailed document that outlines all the finishes in the house (e.g. flooring, walls, roofing, plaster spec). Needed for quote/tender purposes.
Window schedule
Part of the construction drawing, indexing each door and window with sizes. Used to get glazing quote.
NHBRC
National Home Builders Registration Council, government body that supervises building standards.
Runner
A specialist that submits and completes building applications at council on your behalf for a fee. They generally go in every day to check on status and know the ins and outs of the process.
Sub-structure (below ground) building terminology
Foundation
The part of a structure which connects it to the ground, and transfers loads from the structure to the ground. Foundations are generally considered either shallow or deep and consist of concrete with steel reinforcing.
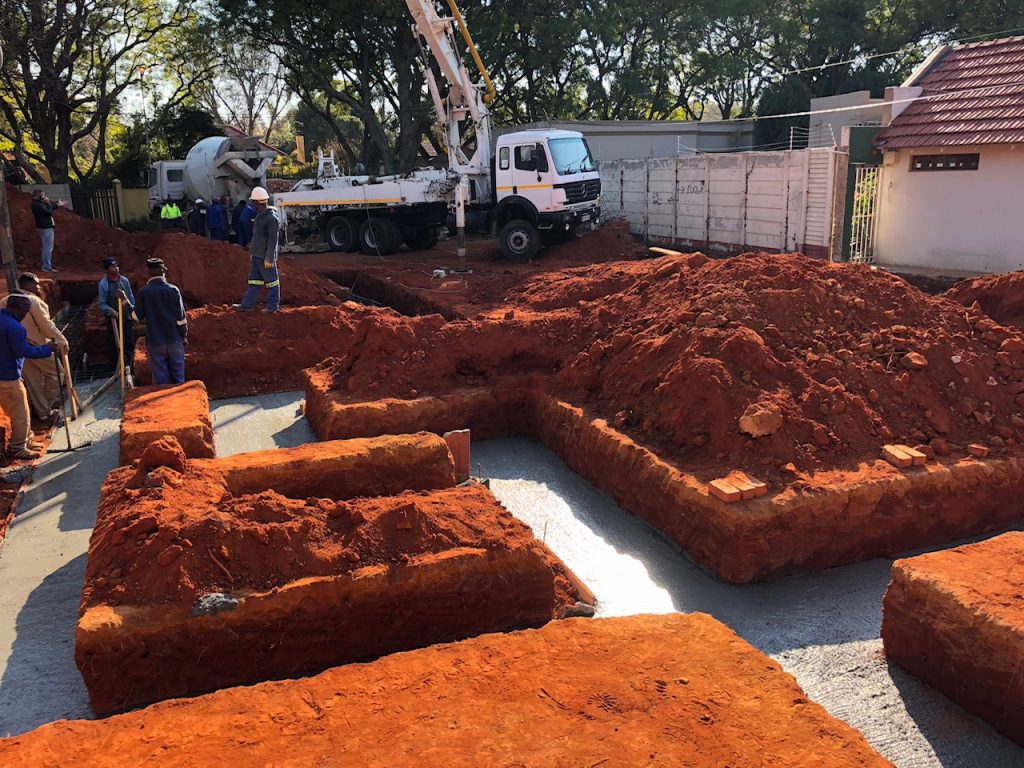

Footing
A part of foundation construction. They are typically made of concrete with rebar reinforcement that has been poured into an excavated trench. The purpose of footings is to support the foundation and prevent settling.
Plinth
Part of a building which separates superstructure and sub structure. Its main functions are to provide level surface for slabs and brickwork, and to transfer load equally to foundations.
Finished Floor Level (FFL)
The final level inside the house once flooring has gone in. These are crucial to get 100% right.
DPC plastic
High density plastic sheet laid underneath ground slabs to avoid damp.
French drain
Is a trench filled with gravel and bidum cloth, containing a perforated pipe that redirects surface water and groundwater away from an area.
Superstructure (main build) building terminology
Slab
A structural element, made of concrete, that is used to create flat horizontal surfaces such as floors, roof decks and ceilings. A slab is generally 15-20cm thick and supported by beams, columns, walls, or the ground.
Dagga (pronounced in English, not Afrikaans)
South African slang for the cement mix or mortar made for building and general repairs.
MPa
Compressive strength which is measured in Megapascal (MPa) for bricks. A good mud-brick has a MPa strength of around 1.6 to 1.9 MPa, while a clay-fired brick has an MPa strength of around 14. Concrete ranges between 15 and 25 MPa.
Concrete also comes in different MPa strengths.
Bagging
Can refer to two wall finishes. Either a light plaster wash over raw bricks, or raw bricks rubbed over (often with a cement bag) while the building cement is still wet.


Brick force
Two main parallel wires joined by in-line welded cross wires. Supplied in rolls and used during bricking for extra reinforcement.
Lintel
A beam placed across the openings like doors, windows etc. in buildings to support the load from the structure above (mostly bought readymade). The width of lintel beam is equal to the width of wall, and the ends of it are built into the wall.
Masonry
Brick and mortar walls.
Formwork
The term used for the process of creating a temporary mould into which concrete is poured and formed. Traditional formwork is created using timber, but it can also be constructed from steel, glass fibre reinforced plastics and other materials.
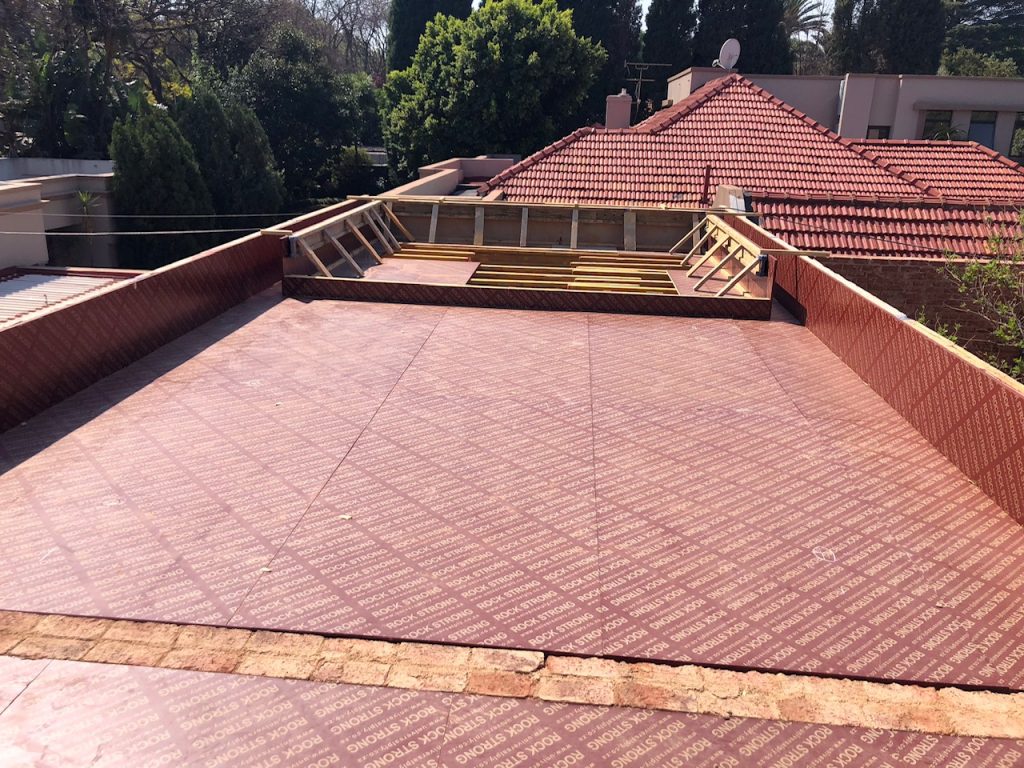

Cast
Inserting concrete into the formwork.
Rebar
Steel bar or mesh of steel wires used as a tension device in concrete and masonry structures to strengthen and aid the concrete under tension.

Conduit
Pipes or tubes (generally plastic) laid down in concrete or in walls before wiring begins, to protect cables.
Glazing
All the glass windows and doors.
Shadowline
A 90 degree strip attached to the ceiling board where it meets the walls. This allows plastering to end just before the junction and provides a neat, recess. If you want a very deep, wide recess, a bulkhead frame will be built.
Carpentry
BIC
Built-in-cupboards, usually constructed to fit measurements on site.
Joinery
Artisan carpentry that involves indoor, ornamental furniture and cupboards, i.e. joiners make BIC.
Carcass
Internal cupboard structure for built-in units, usually constructed out of melamine.
Melamine
Laminated chipboard, used for inexpensive cupboard construction, i.e. carcasses.
Truss
A framework, typically consisting of rafters, posts, and struts, supporting a roof.
Beam
A long, sturdy piece of squared timber or metal used to support the roof or floor of a building.
Joist
A horizontal structural member used across open space, often between beams that subsequently transfer loads to vertical members.
Chromadek
Range of galvanized, steel sheets with epoxy coated colour range for roofing.
Galvanize
Protective coating of zinc on iron or steel to prevent rusting.
Flashing
A strip of metal used to stop water penetrating the junction of a roof with another surface.
Hard wood
More expensive timber for high traffic areas (floor boards) or external application (decks, window frames). Some examples include Balau, Teak and Saligna.
RhinoBoard
Plasterboard used as lining/cladding for ceilings and drywalls.
Rhinolite
A lightweight, finishing plaster for internal application onto brickwork, concrete block, concrete and RhinoBoard.
Supawood
Composite wood that is dense, perfectly flat and used for any joinery that will be painted.
Cornice
An ornamental molding round the wall of a room just below the ceiling.
Skirting
Usually wooden or vinyl board covering the lowest part of an interior wall. Its purpose is to cover the joint between the wall surface and the floor.
Mezzanine
An intermediate floor between main floors of a building, and therefore typically not counted among the overall floors of a building. Often, a mezzanine is low-ceilinged and made from timber.
Painting
PVA/Water based paint
As name suggests, water is the diluent. Best used for walls and ceilings. Easy to apply, less fumes and quick drying.
Solvent/Oil based paint
Mineral spirit is the diluent. Sticky, thick, but durable finish. All surfaces can only be cleaned with turpentine, which adds to the strong vapours. Best for steel and wooden frames or other hard-wearing, external surfaces.
Enamel
Paint that air-dries to a hard, usually glossy, finish, used for coating surfaces that are outdoors or otherwise subject to hard wear or variations in temperature. Now available in both water and oil-based varieties.
General
Gaaitjie
Slang word for small hole. ‘Kap ‘n gaatjie’ – chop a small hole in the wall or concrete. Seems to solve most disasters.
Sparky
Slang word on site for the electrician.
Water reticulation
Infrastructure of pipes which are commonly constructed from plastic, metal or concrete. Water is delivered by making use of the scientific principles of pressure and the energy created delivers the water to its destination.
For more information on a starting a house build, click here.

